Importance of Virtual Machine Migration in Server Virtualization
By now, you should be familiar with Server Virtualization. Migration refers to moving of one virtual machine from one server to another server while it is in production environment, with minimal disruption to any existing sessions. Virtual Machine Migration is done for a number of reasons and we will explore about the same in this article.
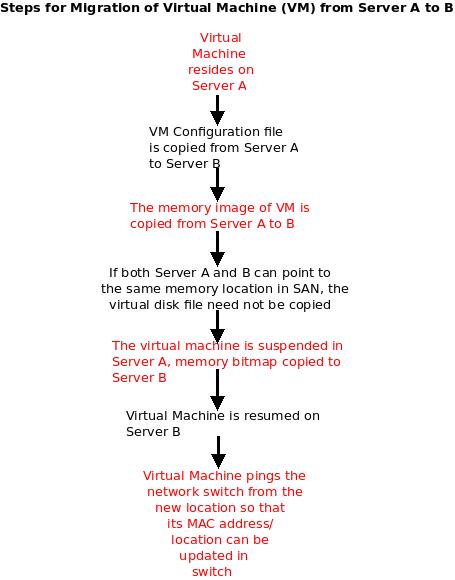 What is Virtual Machine Migration?
What is Virtual Machine Migration?
A Virtual Machine is an independent server module (Operating System + Application) that generally run in independent servers. But with Server Virtualization, its possible to run multiple Virtual Machines in a single (high capacity) server. In this process, each Virtual Machine thinks that it is running on its own server (with dedicated resources).
There are a number of reasons why these Virtual Machines need to be moved from one physical server to another physical server, as explained below. But the process of moving the Virtual Machine from one physical server to another (or one group of physical servers to another) is called Virtual Machine Migration. Most of the popular Server Virtualization applications support this process.
Advantages of Virtual Machine Migration:
- Workloads keep changing dynamically in servers. There is a sudden spike of requests (during month end, for example). Every time it happens, its not possible to provision additional servers manually. So, Virtual Machine Migration accommodates for the changing workloads automatically (It can adapt to both additional workloads or reduced workloads).
- A scheduled maintenance normally results in some downtime for the users of the server. But with Virtual Machine Migration, the VM can be migrated to some other server (for that period of scheduled maintenance) and brought back to the host server after the maintenance is completed.
- Virtual Machine Migration can also migrate Virtual Machines in case of unscheduled server downtime (due to some fault in server), so that users experience high availability of applications at all times.
- Virtual Machine Migration can also be used for Disaster Recovery. This process involves setting up of similar resources in a DR site with high speed WAN links and specialized network connectivity equipment. The Virtual Machines and their memory states are frequently synchronized (replicated) between the primary servers and the servers in the DR site, so that migration can happen quickly in case of a disaster.
- Its easier to migrate a Virtual Machine from one server to another, than migrating the operating system and application(s) individually.
- Using Virtual Machine Migration, its possible to migrate operating systems and applications from older servers to newer servers easily and without disrupting the services.
Salient points you need to know on Virtual Machine Migration:
- The resource allocation (for each virtual machine) are preserved even when they are moved from one virtual machine to another.
- Some vendors provide software tools/ management applications that can identify which hosts (servers) have enough resources to accept migrated VM’s.
- Two identical physical servers may be required for VM migration, but some vendors support migration across servers with disparate hardware configurations too.
- It is important to have sufficient network backbone capacity (bandwidth) in order to move the virtual machines from one server to another, quickly.
- Even during the process of migration, it is possible to maintain network connection and application state, thereby providing continuous uptime to the users.
- The process of brining back the migrated VM to the host server (after server maintenance has been completed, for example) can be automated with some server virtualization products.
- Generally, 64-bit hosts can be migrated to other 64-bit hosts, while 32-bit hosts can be migrated to 32-bit or 64-bit hosts.
- Some server virtualization vendors even allow migration between two servers that have different processor makes.
- Some vendors allow multiple VM’s to be migrated at a time.
- SAN (Storage Networks – Fiber Channel, NAS, iSCSI, etc) are generally recognized and the virtual disk files stored in them are not copied again during migration. Instead, they point to the same location in the SAN.
- Some vendors allow priorities to be set individually for virtual machines to be migrated, so that important VM’s can be given higher priority during migration.
- Logs, of the migration processes are maintained so that it can be accessed later on whenever required.
- Even when the administrator is not physically present, it is possible to schedule migrations to happen at certain times automatically.
excITingIP.com
You could stay up to date on the various computer networking/ related IT technologies by subscribing to this blog with your email address in the sidebar box that says, ‘Get email updates when new articles are published’.