An Overview of Enterprise VPN – Virtual Private Network
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a concept which helps enterprise companies with distributed offices to connect to each other securely over the Internet – In this article, we would touch upon the introduction and advantages of VPN, popular ways of establishing a VPN, types of VPN, advantages of SSL/TLS and IPSec VPN. Read on…
In case you are looking for a short presentation (screen cast) for this article, and you are short of time but have a fast Internet connection, you could also refer to our Youtube presentation (about 10 minutes).
What is a VPN and what are its advantages?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a way to extend the Local Area Network to branch locations and remote locations via the public network (Internet) using technologies like encryption (hence forming secure tunnels between the locations) so that people in the branch/remote locations could access the corporate resources (in head office) in a secure and efficient manner. VPN Networks can be extended from the head office to branch office, home office and even telecommuters/ traveling personnel across the world through the Internet.
Actually, when we send data through the public network (Internet), it mostly travels in clear text, which is easy to sniff by hackers and intruders. That’s why companies connect their various branches by using Leased Lines or MPLS Circuits (which are private networks). But extending such private networks to all the branches could turn out expensive. So, companies have adopted to creating VPN’s between branch and head office networks through the public network (Internet), as Internet can be accessed by a variety of methods (Internet Leased Line, Fixed Broadband Networks, Mobile broadband Networks etc) and is easily available in all locations. The cost of Internet Lines are less when compared to private links like Leased Lines etc.
Advantages of VPN (Virtual Private Networks):
- Since the messages are encrypted, VPN is secure.
- VPN’s are scalable – Thousands of users can connect to the head office simultaneously through the VPN.
- VPN can be extended to any branch/ individual user who has access to Internet via Internet Leased Lines/ Fixed Broadband/ Mobile Broadband etc.
- VPN’s are cost effective, when compared to private networks like Leased Lines and MPLS Circuits.
- VPN helps to centralize all IT resources and allows for centralized administration of critical IT resources at Data Center’s in the head office.
- Remote/ travelling personnel just need to install a VPN client software to access any corporate resources from any location with basic access to Internet (With SSL VPN technologies, even the client software may not be required, just a standard browser will do).
- VPN’s allow for business continuity and faster response from employees during after office hours, holidays and even disasters.
- VPN’s allow for selective access to vendors and partners via an external portal in order to increase their efficiency and get work done faster.
What are the various methods of creating / establishing a VPN?
There are primarily three methods of creating / establishing a Virtual Private Network – With Routers/ VPN Concentrators, With UTM (Unified Threat Management) devices, With Wireless Controllers and Remote Access Points. We have given the architecture diagram for all the three methods of establishing VPN, below:
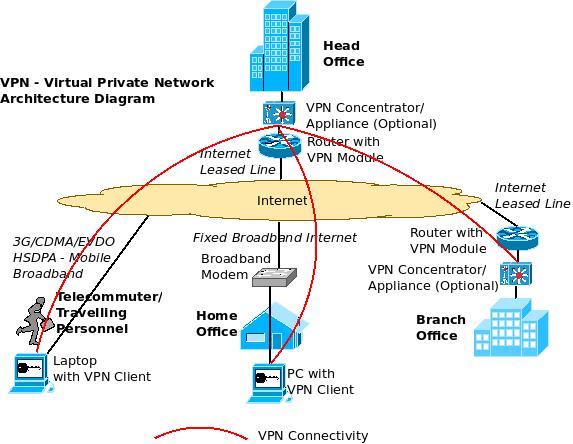
The above diagram shows a scenario where there are four locations (From top, clockwise) – One is the head office (accessing Internet through Internet Leased Lines), another is the branch office (accessing Internet through Internet Leased Lines), yet another is a home office (accessing Internet through Fixed Broadband connection) and we also have telecommuter/ traveling personnel (Accessing Internet through mobile broadband technologies like CDMA/ EVDO/ 3G/ HSDPA etc).
Creating a VPN with Routers/ VPN Concentrators: We can create a Virtual Private Network (VPN) between the head office and other offices either with Routers (at head office and brach office, with VPN Licenses), or through a dedicated VPN Concentrator/ Appliance at these two locations in case the VPN volume is too high and it needs dedicated hardware processing units. For the home office, a VPN client software is loaded to the PC that establishes a VPN with the head office Router/ VPN Concentrator (over the Internet) and we can do the same for the telecommuters/ traveling personnel as well.
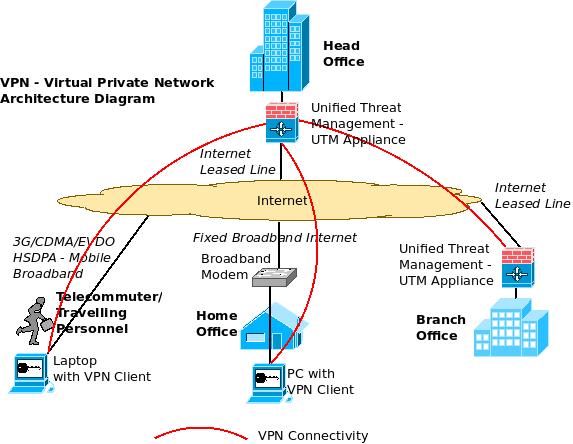
Creating a VPN with UTM (Unified Threat Management Appliance): Like how we created the site to site VPN between the head office and branch office using routers (or VPN Concentrators), we can also use certain UTM appliances (which come with inbuilt VPN Licenses) for establishing site to site VPN. The home office/ traveling personnel can establish a VPN similarly by connecting to the UTM appliances in the head office (through the VPN Client).
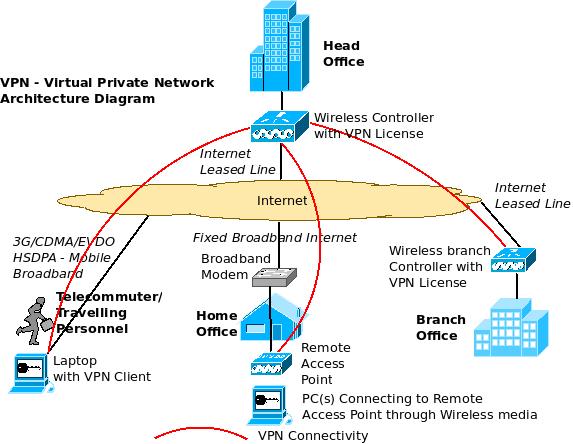
Creating a VPN using Wireless Controller: This is an interesting alternative to above two methods. Here, an enterprise wireless controller (used for centralized management of multiple wireless access points in the enterprise) can itself act as a VPN concentrator (with appropriate licenses) and establish VPN Tunnels with other controllers, remote access points (home office) and VPN Clients (telecommuters/ traveling personnel).
The VPN connections need not always be from the head office to the branch offices / traveling personnel etc as shown in the above diagrams. It can be established from one site to another site, one site to multiple sites and multiple sites to multiple sites depending upon the configuration, models and connection types supported by the various VPN devices. Of course both Site to Site as well as Site to Client VPN’s can be established.
What are the types of VPN?
There are mainly two types of Virtual Private Networks – IPSec VPN and SSL/TLS VPN.
IPSec VPN:
IPSec VPN or Internet Protocol Security VPN is one of the most popular technologies available for establishing VPN over the Internet. It establishes this by using technologies like tunneling, encryption and authentication. This type of VPN assumes that a trusted relationship is present between the various sites or individual computers forming the VPN and it defines procedures to provide data integrity, authenticity and confidentiality across the public network (Internet). IPSec VPN operates in the Network layer.
Advantages of IPSec VPN:
- IPSec VPN is an established and field tested technology and has been in use by majority of the customers for a long period now.
- IPSec VPN is a client based VPN technology and connects to only those sites/ devices which can prove their integrity (This is more applicable for home offices and remote offices where the VPN software client needs to be installed before-hand to establish a secure connectivity back to the head office). So, administrators can be quite sure that the devices connecting to the network are trusted ones.
- Since IPSec VPN inspects and drops a packet at a lower level in the protocol stack (network layer), the packet drop performance is better thereby enabling smooth functioning even in a high capacity usage scenario.
- IPSec VPN’s are the preferred choice of companies for establishing Site to Site VPN and IPSec has found more implementations in this segment. IPSec VPN’s can also establish a Site to Client VPN with devices installed with IPSec clients.
- IPSec VPN basically gives full access to all the head office Intranet applications to branch office/ remote personnel establishing the VPN to HO. So, the user feels as if they are at the office even though they may be working from home. Certain solutions allow selective blocking of certain applications/ devices from being accessed over a remote network.
- IPSec supports multiple methods of authentication and also demonstrates flexibility on choosing the appropriate authentication mechanism thereby making it difficult for intruders to perform attacks like ‘Man in the Middle’ attacks etc.
- Centralized management options for VPN settings are available with IPSec VPN.
- IPSec can implement automatic fail over to another VPN device in case the original one fails.
SSL/TLS VPN:
An SSL VPN uses the Secure Sockets Protocol (SSL) technology to create a virtual private network between various sites and sites to clients using encryption and authentication over the network. Much of this protocol was adapted to Transport Layer Security (TLS) standard as well and hence it is some times referred to as TLS VPN. SSL VPN can provide authentication, authorization, accounting and network access. SSL VPN can provide secure access through standard web browsers enabling VPN’s to be established from any computer connected to Internet. SSL VPN can also provide Site to Site VPN. SSL/TLS VPN operates in the Application Layer.
Types of SSL VPN:
Client-less Access: SSL/TLS VPN’s can provide secure VPN access to the head office from any computer with a standard web browser (with out the need for a pre-installed client on the computer). But this may be limited to accessing web based applications that support browser access.
Client-based Access: To offset the above disadvantage and provide fuller access to applications, SSL/TLS VPN’s automatically download a light weight client upon initial connection to the VPN gateway.
Advantages of SSL/TLS VPN:
- Since SSL/TLS VPN’s support browser based access, corporate resources can be accessed by employees/ partners from any computer with Internet access after proper authentication.
- SSL/TLS VPN’s allow for host integrity checking (checking if the computers trying to establish a VPN connection subscribe to certain standards – like latest OS version with patches, latest version of anti-virus software etc) and remediation (if required) to ensure secure network access.
- Easier to deploy and maintain across a large number of traveling personnel/ remote users as there is no need to install and maintain a VPN client for each machine connecting to the network.
- SSL/TLS VPN can provide granular network access controls for each user/ group of users to limit remote user access to certain designated resources or applications in the corporate network.
- SSL/ TLS VPN supports many types of end point devices like mobile phones, PDA’s, smart phones etc and multiple operating systems.
- Supports multiple methods of user authentication and also integration with centralized authentication mechanisms like Radius/LDAP, Active Directory etc.
- It is possible to have secure user customized web-portals (Extranets) for partners etc with SSL/TLS VPN, as the basic characteristic of SSL/TLS VPN is to provide restricted access to certain applications only, and adding more applications when required, thereby providing granular network access controls.
- SSL/TLS VPN’s are basically designed for Internet browsers and hence do not have any NAT/Firewall traversal issues.
- SSL/TLS VPN’s have exhaustive auditing capabilities which is crucial for regulatory compliance. Log information (regarding which user accessed which resources at what time over which period/date etc) can be taken, stored and analyzed with detailed querying and reporting mechanisms.
- SSL VPN’s can cluster VPN devices both within the LAN as well as across the WAN for improved performance, scalability and redundancy.
- SSL VPN’s are better for disaster recovery/ business continuity as it allows for anywhere anytime access to the corporate networks for authorized users.
Some vendors have implemented VPN solutions where the client would establish a VPN either with IPSec or with SSL/TLS based on the best connectivity parameters required for that session.
Open source VPN: Apart from many commercial products available for VPN, there are also free open source alternatives to establish a VPN between two places like OpenVPN and OpenSSL.You may need a hardware device for running the open source software at both the places.
excITingIP.com
In case you want to add to this discussion, please add a comment below or if you want to contact us, you could do so using the contact form. You could stay up to date on this field – Computer Networking by subscribing with your email address in the box titled ” Get Email Updates when new articles are published”
Hello, I’m very interested in VPN as IT specialist , I need a VPN between me and one friend of mine ,my question is. Is there any free software to make this network? , we are using windows XP Sp2 in the two sides .
Yeah, you can use OpenVPN or OpenSSL. You can also use open source router packages like Vyatta or XORP to create VPN’s among other things. The easiest way would be to buy a low cost router/firewall and use the client provided by the vendor to create a VPN connection. Eg. Cisco Small business/ Fortinet/ Sonicwall etc.
Hello sir, I want a presentation (ppt file) on vpn in a simple an easy language. As i am not able to understand what is vcp and utf in the above diagram. So can u provide me…..
It will be very helpful to me. Thanks…… My email is samk_1123@yahoo.com
I don’t have a presentation on this topic. Did you see the youtube video (link given at the beginning of this article)? Maybe that can help.
Respected sir,
i hereby request to send ppt’s on enterprise wireless network in vpn.
please help me out,i am surfing in net since many days am not getting exact information
i hope you help me out with more information on it..
Thanks lot in advance
Thanks so much for this! Very elaborating, just what I needed.
Thank you so much..its vey much informative.
I am a software professional and we the software team has developed an intranet based web application which is supposed to access remotely from different locations with in the vpn. Here the vpn is established through SonicWall NSA 2400, 240 Series Security devces. we have leased line only with our head office and the NSA 2400 device is being used there to establsh the vpn. rest all locations are with nsa 240 series devices. Our existing VPN establshment is in such a way that one need to use microsoft remote destop connection to connect to the remote locations through vpn. vpn client softwares are not using now. I have a thought in my mind that the way VPN is established is not in a shape to give the maximum advantage of using a VPN. Beause for an example, the user from one location can not access/print remotely to a network printer which is at the other site of VPN. I need the netwrok printers to be accessable from anywhere with in the VPN. I do not have much knowledge in networking.
It would be very helpful if you can advice me with the best methodolgies of establishing a VPN which will solve my stated issues.
Naturally, they desire to support and please as many users as they
can at the same time. This level is found between Layer 2 and Layer 3 (the Data Link Layer as well as the
Network Level respectively).
write a report with an overview of how RECO could use VPN technologies in this type of extranets
Anyone interested to setup his own VPN business without investing in infrastructure? PureVPN has a lucrative solution for entrepreneur.
HI Sir,
I need a advise as we are planning for a centralised network and planning to use MPLS and branches to access resources and internet at HO. is it a right plan of action for cost reduction.
I have used Business VPN by PureVPN which is quite simple and cost effective. For remote access they have provided me with a VPN accounts associated with dedicated IP enabled with “Web protection”. Therefore, only authorize people have access to our office network in california.
Furthermore, I have recently enabled their “Split Tunneling” option which gives control to the owner to restrict any particular website to avoid abusing by employees
Many of VPNs are open source and anyone can buy this for free. And its best to use. I think its free of cost is also one of its advantages.